Clinical Research Meeting 2018

Theme: Strengthening The Bond Of Clinical Research and Medical Practice
Why to Attend???
Who Should Attend and Who You’ll Meet
Major Worldwide pharmacy Organization:
- International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP)
- International Pharmaceutical Students' Federation (IPSF)
- European Association of Employed Community Pharmacists in Europe (EPhEU)
- Pharmaceutical Society of Australia
- Canadian Pharmacists Association
- Chinese Pharmaceutical Association
- Danish Association of Pharmacologists
- Indian Pharmacist Association
- Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland
- Pharmaceutical Society Of New Zealand
- Norwegian Pharmacy Association
- Philippine Pharmacists Association (PPhA)
- National Pharmacy Association
- American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy (AACP)
- American Pharmacists Association (APhA)
For more details: http://www.meetingsint.com/pharma-conferences/clinicalresearch/call-for-abstracts
A drug discovery and drug design is the program that initiates because there is a disease or clinical condition without suitable medical products available and it is this unmet clinical need which is the underlying driving motivation for the project. The initial research, often occurring in academia, generates data to develop a hypothesis that the inhibition or activation of a protein or pathway will result in a therapeutic effect in a disease state. The outcome of this activity is the selection of a target which may require further validation prior to progression into the lead discovery phase in order to justify a drug discovery effort. During lead discovery, an intensive search ensues to find a drug-like small molecule or biological therapeutic, typically termed a development candidate, that will progress into preclinical, and if successful, into clinical development and ultimately be a marketed medicine.
- Research & Development in Drug Designing
- Drug Targets
- Drug Designing Docking
- Structural based drug designing.
- Virtual screening
Clinical Pharmacology involves the study of the actions of drugs and chemicals on cells, tissues and the whole body. It includes finding out how drugs produce beneficial and adverse effects, with the aim of improving the way drugs are tested and to give greater benefit in the treatment of disease. The cellular and chemical abnormalities of disease states are studied in the expectation that molecules may be designed specifically to correct the abnormality. The study of pharmacology requires understanding normal body functions (biochemistry and physiology) and the disturbances that occur (pathology). Pharmacology is the basis of much of the research and development of new drugs. The future of pharmacology is assured, as there remain many diseases for which neither cure nor palliation have been devised - for example, Alzheimer’s disease, neurogenerative diseases, many forms of cancer. Even when a cure or treatment is available, few medicines are perfect and the search for better drugs continues. In addition, other scientists such as physiologists, biochemists and psychologists often find a knowledge of pharmacology useful as they use drugs to probe and define the biological systems they are studying.
- Introduction to Concepts in Pharmacotherapy
- Adverse Drug Reactions
- Drug Interactions and Drug Errors
- Use of placebos in clinical trials and clinical practiceDrug Designing Docking
- Factors Affecting Response to Drugs
- Efficacy and Effectiveness
- Clinical Trials on Drugs used in Various Disorders
Clinical Phase Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are look into contemplates that investigate whether a medicinal procedure, treatment, or gadget is sheltered and successful for people. These investigations likewise may demonstrate which therapeutic methodologies work best for specific sicknesses or gatherings of individuals. Clinical trials create the best information accessible for social insurance basic leadership. The motivation behind clinical trials is look into, so the investigations take after strict logical norms. These benchmarks ensure patients and help create dependable investigation comes about. Clinical trials of biomedical mediations commonly continue through four stages.
Stage I Clinical Trial
Stage I clinical trials are done to test another biomedical mediation without precedent for a little gathering of individuals to assess security.
Stage II Clinical Trial
Stage II clinical trials are done to ponder a mediation in a bigger gathering of individuals to decide adequacy and to additionally assess its wellbeing.
Stage III Clinical Trial
Stage III investigations are done to think about the viability of a mediation in extensive gatherings of trial members by contrasting the intercession with other standard or exploratory intercessions.
Stage IV Clinical Trial
Stage IV ponders is done after mediation has been promoted. These examinations are intended to screen the viability of the affirmed mediation in the all-inclusive community and to gather data about any unfavorable impacts related with across the board use over longer timeframes.
- Clinical research phase studies
- Types of clinical trials
- Clinical trial design
- Patient recruiting & retention
- Risks and benefits of participants
- Preparing data for FDA submission
- Good clinical practice and inspection readiness
Case Report in Clinical Trials
Case Report forms an important part of Clinical Research. A case report form is a document specifically used in clinical trials. It is used as tool by the sponsor of the clinical trial to gather information from each participating site. It comprises of data of each and every patient participating in clinical trials including the adverse events. Case reports may be regarded as an unexpected association between diseases, disorders or symptoms. An unexpected event in the course of observing, treating a patient, possibilities of pathogenesis of a disease or an adverse effect. Unique or rare salient features of a disease or therapeutic approaches or a notable variation of the anatomical structures. Also, there are several case reports like Cancer case reports, Cardiovascular trials case report, Case studies on sexually transmitted diseases, Case studies on type 1 and type 2 diabetes, Case reports on drugs used in pregnancy and lactation.
- Well-Referenced CRFs
- Organizing CRF Fields
- CRF Completion Guidelines
- Eligibility Checklist
- Informed CONSENT/HIPAA Authorization Documentation
- Research Sample Tracking
Pharmacodynamics is the mechanism where drugs exert their effects on the body. To produce therapeutic or toxic effects drugs interact with receptors in the body – the pharmacodynamics phase of drug action. Pharmacodynamics is often referred to as “what the drug does to the body”. In order to exert their effects, drugs usually interact in a structurally specific way with a protein receptor or act on physiological processes within the body. This activates a secondary messenger system that produces a physiological effect. The aim of drug therapy is to reverse any changes so the body can return to its homeostatic state. All bodily functions are a result of interactions of various chemicals and drugs act by interfering with these processes. Drugs usually combine with particular chemicals to modify its effect on the body.
- Overview of Pharmacodynamics
- Drug–Receptor Interactions
- Chemical Interactions
- Dose-Response Relationships
Primary goals of clinical pharmacokinetics include enhancing efficacy and decreasing toxicity of a patient’s drug therapy. The development of strong correlations between drug concentrations and their pharmacologic responses has enabled clinicians to apply pharmacokinetic principles to actual patient situations. A drug’s effect is often related to its concentration at the site of action, so it would be useful to monitor this concentration. Pharmacokinetics is currently defined as the study of the time course of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Clinical pharmacokinetics is the application of pharmacokinetic principles to the safe and effective therapeutic management of drugs in an individual patient.
- Overview of Pharmacokinetics
- Drug Absorption
- Drug Bioavailability
- Drug Metabolism
- Drug safety
Ethnopharmacy is the study which describes that how different medicines are viewed and put to use in a society. Although ethnopharmacy concentrates on traditional or folk medicines used in the society, it also looks at more modern pharmaceutical uses. Ethnopharmacists consider the beginning of pharmaceuticals, whether they are from actually happening or man-made components, to decide how they have come to be acknowledged by a gathering as medicinally valuable. They likewise concentrate how pharmaceuticals are controlled to individuals in the general public and how powerful the pharmaceuticals are at fighting different restorative conditions.
- Ethnopharmacology in drug discovery and development
- Phytochemical, pharmacological, antimicrobial evaluation of medicinal plants
- Identification and documentation of medicinal plants and traditional resources
- Development of analytical techniques for quality control, and standardization of herbal medicine
- IP rights, patents and regulatory affairs of medicinal and aromatic plants
- Conservation & propagation of rare, endangered & threatened medicinal plants
Pharmacovigilance Risk Management
Pharmacovigilance and Risk Management were designed to provide an understanding of risk management in health care manufacturing operations and its applications. Pharmaceutical risk management can impact labeling, regulatory decisions, legal protection, intellectual property, enforcement, marketing, and company reputation. This Pharmacovigilance (PV) Toolkit is a collection of resources and information needed for the practice of pharmacovigilance. The main aim of its development is to ensure that PV practitioners in low- and middle-income countries get access to information on the processes and activities involved in PV from a trusted source. The Toolkit contents are endorsed by the WHO Advisory Committee on the Safety of Medicinal Products after the original text has been written and reviewed by global experts.
- Data collection and verification
- Data entry and Duplicate search
- Coding of adverse reaction descriptions
- Coding of drugs
- Good pharmacovigilance practice
- Quality control in pharmacovigilance processes
Health Care Practitioner role in Patient Safety
Pharmaceutical care can be tendered to individuals and populations. “Population-based Pharmaceutical care” uses demographic and epidemiological data to establish formularies or medicine lists, develop and monitor pharmacy policies, develop and manage pharmacy networks, prepare and analyzed reports of drug utilization/costs, conduct drug utilization reviews and educate providers on medicine policies and procedures. Without individual pharmaceutical care, however, no system can manage drug therapy and monitor medicine-related illness effectively. The population-based functions identified above need to occur either before or after patients are seen and provide valuable information, but cannot replace patient-specific services while patients are being seen. Medicine related illnesses occur frequently even with medicines that are in a system’s formulary or medicines list, since these medicines are often prescribed, administered or used inappropriately. Patients need pharmacists’ services at the time they are receiving care. Successful pharmacotherapy is specific for each patient. It includes individual drug therapy decisions, reaching concordance (an agreement between the patient and the health care provider on the therapeutic outcome and how it may be achieved), and critical patient monitoring activities. For each individual patient’s drug treatment, the pharmacist develops a care plan together with the patient. Patients can then contribute to successful outcomes by taking part of the responsibility for their own care and not relying solely on caregivers, in the former paternalistic style. Pharmaceutical care does not exist in isolation from other health care services. It must be provided in collaboration with patients, physicians, nurses and other health care providers. Pharmacists are responsible directly to patients for the cost, quality and results of pharmaceutical care.
- En Supply correct medication information
- Sure patients have medication access
- Evaluate medication appropriateness
- Improve patients’ medication adherence
- Provide health and wellness services
A definitive motivation behind clinical nursing is quiet care. Clinical nursing research is a methodical investigation into the issues experienced in nursing practice and into the modalities of patient care. Clinical nursing practice without clinical nursing research is clinical nursing practice based on impulses without approval. Clinical medical attendant scientists should endeavor to create organizations with clinical medical caretakers. Therefore, clinical medical attendants will perceive the criticalness of their part in nursing exploration and scientists will understand the advantages of their examination to persistent care.
- Primary and Transitions health care
- Critical care nursing
- Clinical preventive services delivery
- Cognitive interventions and cohort design
- Collaborative research
- Community mental health
- Complementary and alternative practices and products (CAPPS)
Clinical Data Management Statistics
Clinical information administration is the procedure of gathering, cleaning, coordination and administration of subject information in consistence with administrative benchmarks. It is a basic stage in clinical research, which prompts era of high caliber, solid, and factually stable information from clinical trials, this has been encouraged by the utilization of programming applications that keep up a review trail and give simple recognizable proof and determination of information inconsistencies. CDM likewise bolsters the direct, administration and examination of concentrates over the range of clinical research. A definitive objective of CDM is to guarantee that information bolster conclusions drawn from look into. Accomplishing this objective ensures general wellbeing and trust in advertised therapeutics.
- Paper-based and web-based trials
- Electronic Data Capture in full compliance with CFR 21 part 11
- Blind and independent double data entry
- Full electronic Audit Trail
- Computer-generated and fully tracked Data Clarification Forms
- Coding terms using MedDRA for adverse events
- Automated and manual capabilities of clinical data
Bioethics is the study of the typically controversial ethical issues emerging from new situations and possibilities brought about by advances in medicine. It is also moral discernment as it relates to medical policy, practice, and research. Bioethicists are concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, clinical research, and philosophy etc. One of the first areas addressed by modern bioethicists was that of human experimentation. The National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research was initially established in 1974 to identify the basic ethical principles that should underlie the conduct of biomedical and behavioral research involving human subjects.
Clinical research ethics are the set of relevant ethics considered in the conduct of a clinical trial in the field of clinical research. It borrows from the broader fields of research ethics and medical ethics. Quality of clinical trials depends on data integrity and subject protection. Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is the universal ethical and scientific quality standard for conducting clinical trials. The GCP standard applies to all aspects of the clinical trial process.
- Ethics & Human Subject Protection
- Bioethics: Case studies and Ethical regulatory guidelines
- Ethical and regulatory issues
- Compliance and regulatory requirements in clinical research
- Regulatory Inspections of Research Sites
- Techniques for designing case report forms in clinical research
Entrepreneurs in Clinical Research
Entrepreneurs in Clinical Research is designed for the researchers and practitioners who want to learn about idea development, entrepreneurship, and start-up processes within the pharmaceuticals (and related (bio) technologies) area. While intellectual property rights form an important part of the content, the scope of the course is broader than this, emphasizing an overview of entrepreneurship within the area, in which intellectual property constitutes one of a number of aspects. Entrepreneurs are usually viewed as individuals who take substantial risks to go out and start new companies, but most pharmacists go to work for entities that are already established, such as a community pharmacy or hospital. Such positions are generally considered safe, as they promise a steady paycheck and continued employment. For that reason, entrepreneurship is not commonly listed among a pharmacist’s skill sets.
- Business visionaries
- Clinical trials brokers
- Investigator networks
- Key research personnel
- Risks in production and sales
- Profit and loss in the production
Globalization of Clinical Research
Over the last 3 decades, clinical trials have become increasingly globalized. This has especially been the case for cardiovascular outcomes trials. There are many reasons for this phenomenon, but foremost is the growing size and length of clinical heart failure trials. For example, the modern era of heart failure therapy with neurohormonal antagonists was ushered in by the Captopril Multicenter Trial published in 1983, in which 92 patients with refractory heart failure were randomized to captopril or placebo with a primary endpoint of improvement in treadmill exercise time after 3 months of treatment. Surprisingly, even with this small number of patients, a subsequent post-hoc analysis showed a significantly lower mortality rate in the clinical deterioration, and improved symptoms and quality of life. Demonstrating meaningful benefit with an additional agent on current guideline-recommended therapies has become increasingly difficult. Mortality reductions rarely approach the 20% to 30% range over a 1- to 3-year period, necessitating larger and longer trials that can detect much more modest, albeit clinically meaningful, improvements. Given advances in therapy, it has become increasing difficult to include placebo groups, so often an active comparator with known efficacy is utilized, making it more difficult to show an incremental benefit. Alternatively, a noninferiority design may be utilized to ensure that the new therapy is at least as good as another therapy with proven efficacy. This type of trial requires even larger numbers of patients depending on the noninferiority margin selected. With the current focus on drug safety, even larger trials may be required to exclude unexpected safety problems when a novel agent is studied.
- Trends in the globalization of clinical research
- Ethical and scientific questions raised by globalization
- The importance and challenges of considering multinational trials
- CRO/Sponsor
- Clinical investigation plans
- Global regulatory plans
The expanding ailment trouble is impelling the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry to raise new substance elements into the market at a higher rate. Most organizations are outsourcing the clinical trials of their recently created medications to different contract look into associations as this could spare them the bothers of administrative issues and patient enrollment load from the innovative work stage. Clinical trials enable the medication to be tried for wellbeing by various ethnic populaces. Because of the higher therapeutic needs and expanding malady predominance, creating nations are turning into a center point for clinical trial execution. Since 2006, there has been an expanded number of trials enrolled worldwide and it is evaluated to increment facilitate in the coming years, which would add to the market development.
Japanese pharmaceutical market to witness moderate growth up to 2021
The Japanese human services showcase is described by abnormal amounts of reasonableness and simple access to social insurance administrations.Essential variables to drive the market development amid the conjecture time frame will be the expanding weight of the elderly populace and administrative rules of the nation. The variables that will control development, in any case, will be the expiry of licenses of high-turnover tranquilizes later on, bringing about nonexclusive substitutes and yearly value cuts. Patent expiry is additionally anticipated that would influence the incomes of a portion of the real pharmaceutical organizations in Japan. For instance, the licenses for Daiichi Sankyo's Olmesartan group of hostile to hypertensive items in the US terminated in 2016 and are expected for expiry in the EU and Japan this year. The items represented 28.8% of the organization's incomes in 2016.
The administration likewise plans to issue new administrative rules to speed up the endorsement procedure of items and increment access to novel therapeutics. A portion of the rules incorporate the utilization of information from Phase III clinical trials did in areas other than Japan. The rules are required to draw in outside organizations, as well as drive development in the market.
Japan is a mixed bag of fortunes for pharmaceutical companies
Pharmaceutical organizations confront many difficulties in Japan as far as its complex administrative and evaluating process and the standard value cuts which posture obstacles for the presentation of new imaginative medications. These have kept the general market measure dormant, developing by just 1% of every 2012, as indicated by Data monitor Healthcare's Company Analysis. A standout amongst the most huge difficulties confronted by pharmaceutical organizations in the Japanese market is the act of biennial value cuts, which imply that the cost of a medication can normally just reduction following dispatch. A further exacerbating component is expanding generics take-up, following a heap of professional generics measures presented since 2007. In spite of these difficulties, the world's second biggest pharmaceutical market shows various open doors, including a maturing populace, together with a generally low obstruction to repayment contrasted with numerous EU markets.
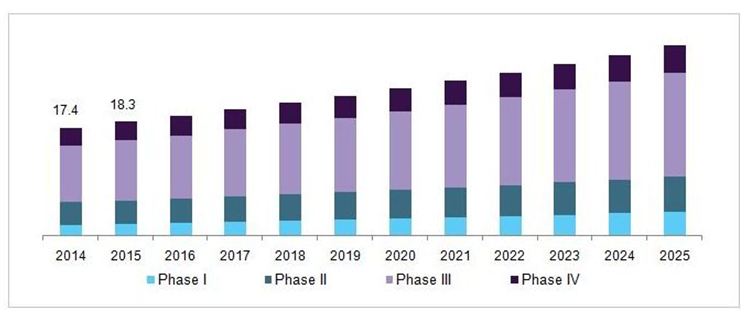
The clinical trials showcase has been evaluated to achieve USD 14.2 billion out of 2016 and is anticipated to stretch around USD 22 billion by the year 2021, developing at a CAGR (aggravated yearly development rate) of 7.5%, amid the conjecture time frame 2016 to 2021. Clinical trial is a piece of clinical research that takes after a directed convention. Clinical trials are essentially performed to get information on security and adequacy of the new created sedate. Clinical trial information is obligatory for promote endorsement of the medication and to bring it into the market.
U.S. clinical trials market, by phase, 2014 - 2025 (USD Billion)
Asia is one of the quickest developing markets. India, China, Singapore and South Korea are the real players engaged with this market. This high development is credited to the way that the cost associated with playing out a trial is less and the enormous area it gives in the part of sicknesses and patients.
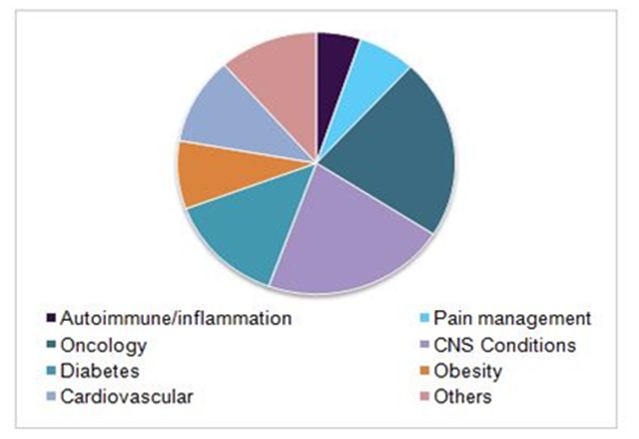
Global clinical trials market, by indication, 2016(%)
Patent expiries will build bland substitution, which is additionally being advanced by the Japanese government to control costs and decrease the weight of social insurance use. Likewise, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare has declared plans to audit tranquilize costs yearly from December 2016, rather than once like clockwork.
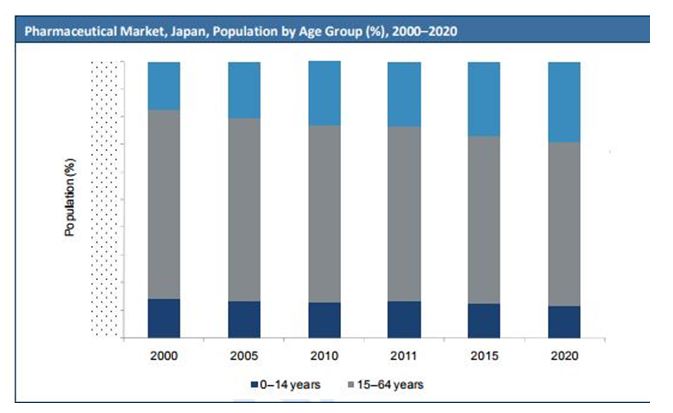
COMPARISON BY AGE GROUP VS YEARS, JAPAN
In fact, the Japanese repayment framework is streamlined contrasted with the convoluted procedures organizations need to experience in different nations, with pharmacoeconomics once in a while used to settle on posting choices. Likewise, measures taken by the medication administrative experts to diminish the slack time frame regarding new medication endorsements contrasted with the US and the EU are starting to yield comes about, with the quantity of new medications affirmed in Japan on the ascent in the course of recent years.
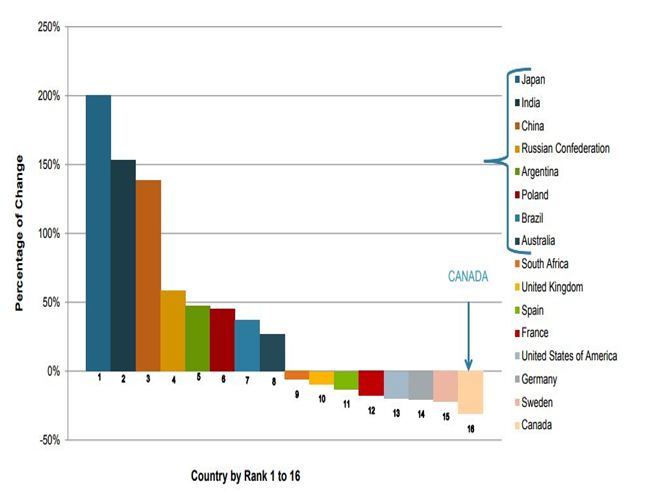
CLINICAL RESEARCH TRENDS BY REGIONAL OUTLOOK
Report Scope
| Attribute | Details |
| Base year for estimation | 2016 |
| Actual estimates/Historical data | 2014 - 2016 |
| Forecast period | 2017 - 2025 |
| Market representation | Revenue in USD Million & CAGR from 2017 to 2025 |
| Regional scope | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Central & South America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country scope | U.S., Canada, UK, Germany, China, Japan, Brazil, Mexico, South Africa |
| Report coverage | Revenue, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors, trends |
References:
- https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/clinical-trials-market
- http://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/researchreports/researchreportreport-japanese-pharmaceutical-market-to-witness-moderate-growth-up-to-2021-5753353/
- https://pharmaintelligence.informa.com/~/media/Informa-Shop-Window/Pharma/Files/PDFs/whitepapers/Japan-white-paper_11-2016.pdf
- https://www.marketresearch.com/product/sample-7544798.pdf
- Drug Discovery and Drug Design
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Clinical Phase and Clinical Trials
- Case Report in Clinical Trials
- Pharmacodynamics
- Pharmacokinetics
- Ethnopharmacy
- Pharmacovigilance and Risk Management
- Clinical Nursing Research
- Clinical Data Management and Statistics
- Bioethics and Quality Regulation
- Entrepreneurs in Clinical Research
- Globalization of Clinical Research
- Health Care Practitioner role in Patient Safety
- International Journal of Drug Development and Research
- Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Research