
Genetics 2019
Theme: Innovation & Ideas in the field of Genetics and Molecular Biology
Building on the strong connection and networking at our previous meetings, we are pleased to announce that the 3rd International Genetics and Molecular Biology Conference is scheduled for October 14-15, 2019, at the Brussels, Belgium. Genetics 2019 is unique in the genetic and molecular biology field, as it is focused on the technological challenges and engineering solutions for the robust and cost-effective manufacturing of cell and gene therapies. Moreover, welcoming location and overall format, this conference is a valuable opportunity to showcase new and existing approaches with key academic and industrial leaders.In addition to a comprehensive series of oral session’s speakers from academic and industrial groups, we have designed the conference to foster networking and facilitate informal discussion around key engineering advances and issues. This will be enabled via several poster sessions, informal drinks and a focused workshop on viral manufacturing challenges & next generation technologies.
About Brussels
Brussel is the capital city of Belgium and of Brussels Capital Region. It is entirely surrounded by Dutch-speaking Flanders and its constituent Flemish Brabant province. As headquarters of many European institutions, Brussels might also be considered something of a capital for the European Union. Being at the crossroads of cultures (the Germanic in the North and the Romance in the South) and playing an important role in Europe.The population of the city of Brussels is 1 million and the population of Brussels metropolitan area is just over 2 million.Brussels weather can often be grey and humid with a high and fairly evenly distributed annual average rainfall of 820 mm (32 in) and on average approximately 200 days of rainfall per year. Daily differences between average highs and average lows don't exceed 9ºC (16ºF). Brussels main airport is Brussels Airport, locally still commonly referred to as Brussels National or Zaventem.
Target Audience
Genomic Students, Genomics Researchers, Genomics Faculty, Genomics Scientists, Genomics Colleges, Pharmacology Scientists, Pharmacology Health Professionals, Genetics Associations and Societies, Geneticists, Genetic Counsellors, Bio pharmacists, Business Entrepreneurs, Training Institutes, Software developing companies, Data Management Companies.
Session 1: Genetics
Genetics is the study of heredity. Heredity is a biological process where a parent passes certain genes onto their children or offspring. Every child inherits genes from both of their biological parents and these genes in turn express specific traits. Some of these traits may be physical for example hair and eye color and skin color etc. On the other hand some genes may also carry the risk of certain diseases and disorders that may pass on from parents to their offspring.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 2: Molecular Biology
Molecular biology chiefly concerns itself with understanding the interactions between the various systems of a cell, including the interrelationship of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis and learning how these interactions are regulated. Molecular biology is the study of molecular underpinnings of the process of replication, transcription and translation of the genetic material. The central dogma of molecular biology where genetic material is transcribed into RNA and then translated into protein, despite being an oversimplified picture of molecular biology, still provides a good starting point for understanding the field.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 3: Plant Genetics and Plant Molecular Science
Plant genetics deals with heredity in plants, specifically mechanisms of hereditary transmission and variation of inherited characteristics. Somatic mutations can contribute to the germ line more easily as flowers develop at the end of branches composed of somatic cells; polyploidy is more common; and plants additionally contain chloroplastic DNA.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 4: Stem Cell Biology
Stem cells have the unique capacity to self-renew and differentiate into a wide array of more specialized cells during development, but also to maintain homeostasis and to support tissue regeneration. Thus stem cells and their more differentiated derivatives are attractive models for studying development and disease, and represent a potential source for cell replacement therapies.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 5: Human Genetics
Human Genetics includes gene structure and organization; gene expression; mutation detection and analysis; linkage analysis and genetic mapping; physical mapping; cytogenetics and genomic imaging; genome structure and organization; disease association studies; molecular diagnostics; genetic epidemiology; evolutionary genetics; developmental genetics; genotype-phenotype relationships; molecular genetics of tumorigenesis; genetics of complex diseases and epistatic interactions; ethical, legal and social issues and bioinformatics.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 6: Bioinformatics in Genetics
The raw material of bioinformatics is the genetic data and the related gene expression. Genetic Data is the entire DNA properties of an organism, both heritable and inheritable.The approach to study these properties was mostly indirect (linkage analysis, karyotyping etc.), sequencing technology replaced these approaches in our century. Sequencing is pointing the nucleic acids (A, T, C, G, U) in correct order that forms a nucleic acid polymer (DNA/RNA)
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 7: Cell Biology
Cell biology is the study of cell structure and function, Focusing on the cell permits a detailed understanding of the tissues and organisms that cells compose. Some organisms have only one cell, while others are organized into cooperative groups with huge numbers of cells. On the whole, cell biology focuses on the structure and function of a cell.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 8: Pharmacogenetics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of how genes affect a person’s response to drugs. Many drugs that are currently available are “one size fits all,” but they don't work the same way for everyone. It can be difficult to predict who will benefit from a medication, who will not respond at all, and who will experience negative side effects. The field of pharmacogenomics is still in its infancy. Its use is currently quite limited, but new approaches are under study in clinical trials. In the future, pharmacogenomics will allow the development of tailored drugs to treat a wide range of health problems, including cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer disease, cancer, HIV/AIDS, and asthma.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 9: Biomarker
Biomarkers are molecules that indicate normal or abnormal process taking place in your body and may be a sign of an underlying condition or disease. Various types of molecules, such as DNA (genes), proteins or hormones, can serve as biomarkers, since they all indicate something about your health.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 10: Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering is the act of modifying the genetic transplantation, transfection of synthetic chromosomes or viral insertion. Selective breeding is not considered a form of genetic engineering makeup of an organism.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 11: Proteomics & Metagenomics
Proteomic analysis (proteomics) refers to the systematic identification and quantification of the complete complement of proteins (the proteome) of a biological system (cell, tissue, organ, biological fluid, or organism) at a specific point in time. Mass spectrometry is the technique most often used for proteomic analysis.
The collective genome of microbes from environmental samples - providing information about microbial diversity and ecology in specific environments. Shotgun metagenomics refers to the method of cutting DNA extracted from environmental samples and sequencing small fragments.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Session 12: Future Trends in Genetics & Genomic Market
Although animal genetics studies have been on-going for over two decades, only recently have comprehensive human twin studies and large-scale association studies been performed. Here, I review recent and accelerating progress in, and continuing challenges to, the identification of genes contributing to such variability. Success in this endeavour will hopefully lead to both better management of pain using currently available therapies and the development and/or prioritizing of new ones.
The growth of the overall market for genomics can be attributed to the growing demand for personalized medicine, growing investments, grants, and funds by the government; rise in research activities in the field of genomics; increasing number of start-up companies; and increasing application of genomic sequencing in the diagnostics.
Genetics Conference | Molecular Biology Conference | Genetics & Molecular Biology Workshop | Stem Cell Biology Meeting | Human Genetics Conference | Cell Biology Symposium | Pharmacogenetics Conference | Microbial Genetics Forum | Genetics and Molecular Biology Event
Introduction:
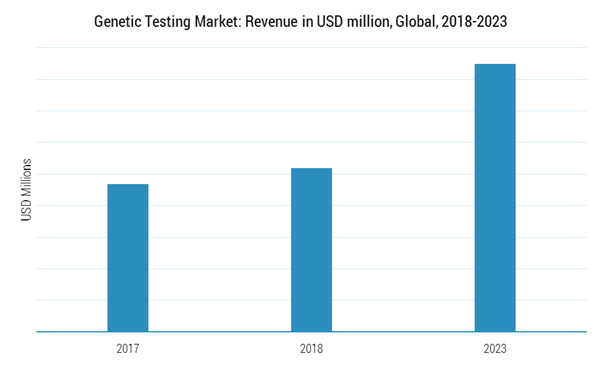
Genetic Testing Market size was valued at USD 10.6 billion in 2017 and is expected to witness more than 11.6% CAGR from 2018 to 2024. Increasing demand from patients for personalized medicines will fuel the demand for genetic testing during the forthcoming years. Personalized medicine offers tailored medical treatment to patients based on their molecular basis. Various developed economies such as Europe undergo genetic testing for detection of various genetic and rare diseases. Detection of diseases at an early stage facilitates early treatment and helps reduce severity of diseases. Growing adoption of personalized medicines coupled with increasing awareness regarding early diagnosis of disease will boost the industry growth over the forecast period.
Importance and Scope:
As of 2017, the global genetic testing market was valued at USD 7,849 million and is expected to record a CAGR of around 11.5% during 2018-2023. In 2017, the North American genetic testing segment of the market studied accounted for the highest revenue and Asia-Pacific is expected to register the highest CAGR of 12.5% over the forecast period. Personalized medicine, where tailored therapy is made available to patients with an understanding of the molecular basis of diseases, has become popular over the recent years.Genetic testing and genome sequencing are two of the most important tools that are used to understand the molecular basis of a disease. Detection of diseases at early stage allows patients to undergo therapeutic treatment at an early stage and minimizes the severity of diseases leading to reduced mortality rate. European countries are screened for several genetic diseases, as an early detection of these diseases can prevent the onset of symptoms, or minimize the severity of the disease. Genetic testing for cancer diagnosis can indicate the predisposition of the disease in the gene, before its actual manifestation. This type of diagnostic technique enables a person to take precautionary steps, and avoid possible risks in the future. Technological advancement in genetic testing is expected to drive the genetic testing market during the coming years.
Global Market on Genetics:
The demand for genetic testing is increasing across the globe owing to the availability of new tests as well as advancement in the genetic testing techniques. Innovations in tests that offer safer and efficient techniques of disease detection, surpassing the risk of miscarriage during early stages of pregnancy will serve to be a high impact rendering factor that will drive the genetic testing market growth during the forthcoming years. The genetic testing market is segmented by treatment type, diseases, technology, and geography. By geography, the market has been segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and South America. Diagnostic testing segment accounted for the highest market share with a revenue share of USD 5690.6 million and is expected to grow at a significant rate over the forecast timeframe owing to its wide applications in various diseases. Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases worldwide will augment the segment growth over the forecast period. Industry players are focusing on strategic expansion through acquisitions, mergers and collaborations help the players to strengthen and enhance the product portfolio. Increasing adoption of genetic testing for early detection of diseases and identification of genetic mutation prior to its manifestation will further augment industry growth over the forecast period.
Future Scope of Genetics:
The industry is expected to witness rapid growth in the future owing to rising physician adoption of genetic testing into clinical care. Availability of regulatory support for direct to consumer testing and on-going advancements in technology enable industry players to maintain their market position. Cancer diagnosis segment dominated the genetic testing market with revenue of USD 5562.8 million in 2017. Around 8.9 million cancer deaths were recorded in 2016, of which around 5%-10% were caused by inheriting genetic mutation. Rising prevalence of various types of cancer such as prostate cancer, breast cancer and lung cancer coupled with increasing awareness pertaining to early detection of cancer will stimulate the market growth throughout the forecast period. Owing to the presence of well-established healthcare facilities and new discoveries in the field of genetic markers.
Some of the eminent industry players operating in global genetic testing market are:
Abbott Molecular, United States Of America
Bayer Diagnostics, United States Of America
Biocartis, Belgium
BioHelix, Taiwan
BioMerieux, France
BGI,China
Celera Genomics, United States Of America
Cepheid, Counsyl, United States Of America
deCODEme, Iceland
Genentech, United States Of America
Genomictree, South Korea
Genomic Health, United States Of America
HTG Molecular Diagnostics, United States Of America
IntegraGen, France
LabCorp Diagnostics, United States Of America
Luminex, United States Of America
Eurofins Scientific, Luxembourg
Centogene AG, Germany
ThermoFisher Scientific, USA
Elitech Group, France
Genomics Related Socieites:
American Society of Human Genetics, USA
European Society of Human Genetics, Austria
Japan Society of Human Genetics, Japan
Genetic Society in China, China
Hong Kong Society of Medical Genetics, Hong Kong
Argentine Society of Medical Genetics, Argentine
Ibero-American Society of Human Genetics of North America, USA
Major Marketing Associations in Europe:
European Letterbox Marketing Association, UK
European Marketing Confederation (EMC), Belgium
European Sales & Marketing Association (ESMA), Ireland
European Marketing Academy, Belgium
Conclusion:
The Asia-Pacific market is expected to register the highest CAGR, as government and private firms are making significant investments in the healthcare industry. Over the last couple of years, to invest in the Japanese market, several mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations between companies have taken place.
Reference:
www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/genetic-testing-market
www.transparencymarketresearch.com/genetic-analysis-services-market.html
- Genetics
- Molecular Biology
- Plant Genetics and Plant Molecular Science
- Stem Cell Biology
- Human Genetics
- Bioinformatics in Genetics
- Cell Biology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Biomarker
- Genetic Engineering
- Proteomics & Metagenomics
- Future Trends in Genetics & Genomic Market
- Journal of Genetic Disorders & Genetic Reports
- Journal of Proteomics & Enzymology
6 Organizing Committee Members
2 Renowned Speakers
Ousman Bajinka
University of The Gambia
Gambia
Randa Talaat
El- Sadat City University Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
Egypt



























































































































