
Bio-technologists meetings 2018

Theme: Contemporary Challenges and profound innovative solutions for a sustainable Bio-world
Meetings International welcomes you to attend the International Meeting on Biotechnology which is to be held during May 07-08 2018, Tokyo Japan. Special interest and theme of the conference is “Contemporary Challenges and profound innovative solutions for a sustainable Bio-world”. Biotechnology Meetings 2018 Prime motto is it will cover the translational nature of biotechnological research, with emphasis on both the basic science as well as its applications in industry and academia. Presentations will include major research advances in Biotechnology, Business development, Strategic alliances, Partnering trends, Product opportunities, Growth business models and Strategies, Licensing and Pharmaceutical Biotechnology (e.g. vaccines, CNS, cancer, antibodies), Medical Biotechnology, Industrial Biotechnology, Bioprocess engineering, Agricultural Biotechnology, Enzyme engineering, Environmental technologies, Transgenic plant and Crops(GM Crops), Bioremediation and Microbial diversity research. Throughout the course of the two day conference, you will have the opportunity to both network and hear leaders from the International academic and Corporate Biotechnology communities.
Biotechnology Meeting 2018 is a multidisciplinary program with broad participation of members from around the Globe focused on learning about innovations and advancements in Biotechnology. This is your best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from Biotech community that is from academia, Research entities, Biotech societies, related associations and also from Government agencies, Exploration and Production industries.
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy Scientists & Students
Biotechnology Researchers
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy Faculty
Biotechnology, Bioscience & Bioeconomy Colleges
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy Associations
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy Society
Business Entrepreneurs
Training Institutes
Bio Industries and Bio Institution
R&D Heads from Institution and Industries
At its simplest, biotechnology is technology based on biology - biotechnology harnesses cellular and bio molecular processes to develop technologies and products that help improve our lives and the health of our planet. We have used the biological processes of microorganisms for more than 6,000 years to make useful food products, such as bread and cheese, and to preserve dairy products. it the use of living systems and organisms to develop or make products, or "any technological application that uses biological systems, living organisms, or derivatives thereof, to make or modify products or processes for specific us Depending on the tools and applications, it often overlaps with the (related) fields of bioengineering, biomedical engineering, bio manufacturing, molecular engineering, etc. Biotechnology has applications in four major industrial areas, including health care (medical), crop production and agriculture, nonfood (industrial) uses of crops and other products (e.g. biodegradable plastics, vegetable oil, biofuels), and environmental uses.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Medical biotechnology is the use of living cells and cell materials to research and produce pharmaceutical and diagnostic products that help treat and prevent human diseases. It is also used to modify the activity of proteins by acting on their genes. The role of biotechnology in medicine has been extensively used in the development of health products and diagnostic tools. The field medical biotechnology keeps growing with new discoveries and products. Medical biotechnology application is the production of antibodies for treating various bacterial infections; these antibodies are produced by using microorganisms. It is also used to modify the activity of proteins by acting on their genes.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Agricultural biotechnology is that the term utilized in crop and stock improvement through biotechnology tools. Biotechnology is outlined as a group of tools that uses living organisms to create or modify a product, improve plants, trees or animals, or develop microorganisms for specific uses and processes have been used in creation of agricultural biotechnology products. Traditional applications include bread making and the fermentation of fruits and grains to make wine and beer. The new phenomenon of Agri Biotech is the idea of modernizing agriculture with the improvements of biotechnology process. Scientific breakthroughs, such as the development of biotechnology applications, help facilitate agricultural research. Some of the green biotechnology examples are horticulture; tissue cell culture reduced the time required for developing new plant varieties. Also, gene transfer technologies enabled researchers to tailor crops for specific uses, such as crops that are resistant to disease, pets, or harsh environmental conditions; that are more nutritious; or that improves food processing.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Environmental biotechnology is a system of scientific and engineering data associated with the utilization of microorganisms and their merchandise within the preservation of environmental pollution through bio-treatment of solid, liquid and gaseous waste. Environmental biotechnology applications are the bio degradation of organic matter of municipal wastewater and biodegradation/detoxification of hazardous substances in industrial wastewater. Other application of environmental biotechnology are the prevention of pollution and restoration of water quality in reservoirs, lakes and rivers, costal area, in aquifers of ground-water, and treatment of potable water. The areas of biotechnology also include tests of toxicity and pathogenicity, biosensors, and biochips to monitor quality of environment, prevent hazardous waste production using biotechnological analogs.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Industrial biotechnology also known as white biotechnology is the application of nature’s toolset for the production of bio-based chemicals, materials and fuels. A cell may be used to generate carbon dioxide, cells and other molecules. It will use energy to accomplish its industrial purpose and also use some energy to get waste (like acetic acid) rather than desired product. This technology also has beneficial effect on greenhouse gas emissions and at the same time supports the agricultural sector. Industrial biotechnological processes use fermentation technology for the use of microorganisms to convert basic raw material to wide range of products. The vital goal in Industrial biotechnology is decreasing waste production that is formed during the process. If developed to its full potential, industrial biotechnology may have a larger impact on the world than health care and agricultural biotechnology.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Bio process engineering also known as bio chemical engineering has usually meant the extension of chemical engineering principles to systems using a biological catalyst to bring about desired chemical transformations. It deals with biological and chemical processes involved in all areas, not just for a particular substrate or species (feedstock or intermediate), outcome or product. It intercepts chemical, mechanical, electrical, environmental, medical, and industrial fields, applying the principles to designing and analysis of processes based on live cells, sub components of cells, as well as non-living matters. It also deals with both micro scale (cellular/molecular) and large scale (systemwide/industrial) designs and analyses.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Biotechnology of plants is the culture of plant cells or tissues and organs in artificial media. Every living cell of a plant should contain all the genes the plant has and thus has the capacity to grow back to a full plant (i.e.) called cell totipotency. Some examples of the current applications in agriculture are micro propagation, somatic embryogenesis, virus and pathogen elimination, embryo rescue, storage and plant modification by somatic clonal variation and genetic engineering. Plants provide us with many pharmaceuticals and industrial compounds. As our population grows, our needs also grow. To increase the quantity of crop production as well as to produce specific characteristics in plants, biotechnologists are using selective gene techniques. The two major methods of propagation are:
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Molecular engineering is property directed synthesis of large molecules and molecular assemblies. At present the development in this field of superamolecular chemistry is rapid. The other aspect of molecular engineering is the transition from superamolecular to materials. This is very active scientific field emerging and it will be most important in future. It could lead to great advances in computational devices and in the ability to manipulate biological materials and development of the ability to design protein molecules will open a path to the fabrication of devices to complex atomic specifications, thus sidestepping obstacles facing conventional micro technology. Molecular Entomology is a branch of molecular biology, the study of various aspects of Insect Science and its application to research and development in plant, human, animal and environment health.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Enzyme engineering involves immobilized or stabilized enzymes, new classes of enzymes (ribozymes) or new enzymatic routes that produce important organic compounds. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins) poised to replace inorganic catalysts, which are used in chemical industry. Proteins are abundant biological entities made up of twenty amino acids strung together by a special type of thread- a chemical bond called the peptide bond. One protein differs from another in the total number of amino acids and their sequence in the chain. Enzymes are Nature’s catalysts, tremendously accelerating the rates of a wide range of biochemical reactions, often with exquisite specificity. Harnessing enzymes for other purposes usually requires engineering them to improve their activity or stability. One approach to engineering enzymes is to make specific modifications, but this demands a detailed and frequently unattainable understanding of the relationship between sequence and function.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Food biotechnology uses plant cells for the production of food flavor and colors, these cells are used in immobilized form and are also used for the production of food additives and supplements. Food technology (national diploma) is the scientific study of the large-scale production and preservation of foods as well as the development and analysis of foodstuffs in industrial food processing facilities. Food producers can use new biotechnology to produce new products with desirable characteristics. These include characteristics such as disease and drought-resistant plants, leaner meat and enhanced flavor and nutritional quality of foods. This technology has also been used to develop life-saving vaccines, insulin, cancer treatment and other pharmaceuticals to improve quality of life. The application of biotechnology in the food sciences has led to an increase in food production and enhanced the quality and safety of food. Food biotechnology is a dynamic field and the continual progress and advances have not only dealt effectively with issues related to food security but also augmented the nutritional and health aspects of food.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Marine biotechnology is also defined as industrial use of living organisms or biological techniques developed through basic research. It is also an innovative field of research in science and technology concerning the support of living organisms with marine products and tools. Molecular biology is playing a major role in marine biotechnology for an understanding of genome level. The knowledge of metabolic pathways and their genomics is the novel way to understand the mechanism behind the production of the compounds. Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the sea or other marine bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Nano biotechnology is that branch of nanotechnology that deals with biological and biochemical applications or uses. Nano biotechnology often studies existing elements of living organisms and nature to fabricate new Nano-devices. Generally, Nano biotechnology refers to the use of nanotechnology to further the goals of biotechnology. Some of the innovative challenges in the field of biology are: New molecular imaging techniques, Quantitative analytical tools, Physical model of the cell as a machine, Better ex-vivo tests and improvement in current laboratory techniques and better drug delivery systems. The Unit is also developing nanoparticle/drug conjugates with the aim of producing targeted drug delivery systems for the treatment of diabetes, HIV and cancer.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Stem cells are defined as having the capacity of self-renew and ability to generate differentiated cells. The origin of these stem cells is from Embryonic Stem (ES) cells. More explicitly, stem cells can generate daughter cells identical to their mother (self-renewal), as well as produce progeny with more restricted potential (differentiated cells) and also stem cells include its replication capacity and potency. The degree of differentiation of stem cells to various other tissue types varies with different types of stem cells and this is called as Plasticity. Plasticity can range different forms like Pluripotency, Multipotency, Totipotency, Unipotency.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Tissue engineering / regenerative drugs is emerging multidisciplinary field involving biology, medicine, and engineering that's possible to revolutionize the ways that we have a tendency to improve the health and quality of life for voluminous individuals worldwide by restoring, maintaining, or enhancing tissue and organ function. Additionally the therapeutic application, wherever the tissue is either mature in an exceedingly patient or outside the patient and transplanted, tissue engineering will have diagnostic applications wherever the tissue is created in vitro and used for testing drug metabolism and uptake, toxicity, and pathogenicity.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Animal biotechnology provides the basis of studying the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and product formation in controlled conditions. This animal biotechnology is used to rapidly multiply animals’ desired genotypes or to introduce specific alterations in their genotypes to achieve useful goals. Animals are often used to help us understand how new drugs will work and whether or not they'll be safe for humans and effective in treating disease. Animal biotechnology now a days based on science of genetic engineering, it existing in other technologies such as transgenic and cloning that are used in animal biotechnology.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Algal biotechnology is a technology developed using algae. The objective of the Micro algal Biotechnology Group is to further the understanding of the ecology of microalgae. This will assist with the development of commercial-scale micro algal culturing techniques for the production of bioactive compounds, aquaculture feed, fine chemicals, and renewable fuels. Additionally, environmental applications such as CO2 bioremediation, control of excessive algal growth and development of management strategies for water supply managers are investigated. Transgenesis in algae is a complex and fast-growing technology.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Fermentation technology is the process of growing microorganisms in large scale and used to produce commercial products or carry out important chemical transformations. Fermentation also results in the production of energy in the form of ATP molecules. There are five major groups of commercially important fermentation, those that produce microbial cells (or biomass), microbial enzymes, microbial metabolites, recombinant products and those modify compounds (i.e.) transformation process. Fermentation is the process developed for manufacturing vast range of materials from chemically simple feedstock, such as ethanol to highly complex proteins. Fermentation technology has contributed much to the well-being and wealth of human populations over millennia; it will continue to do an even greater extent in future.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Pharmaceutical biotechnology is defined as a science covering all technologies required for the production, manufacturing, and registration of biotechnological drugs. They can deal with targets in humans that are not accessible with traditional medicines. It is a multidisciplinary scientific field undergoing an explosive development. Advances in the understanding of molecular principles and the existence of many regulatory proteins have established biotechnological or therapeutic proteins as promising drugs in medicine and pharmacy. Specific therapeutic proteins can be synthesized in non-biological ways, and recombinant proteins can be isolated from complex mixtures in commercially viable processes. More recent developments in biomedical research highlight the potential of nucleic acids in gene therapy and antisense RNAi technology that may become a medical reality in the future.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Proteomics is the study of proteome, the protein complement of genome. Genomics is the study of genome, which describes the entire collection of genes in in organism. There is development of user-friendly browser based bioinformatics tools to extract information about all the possible genomes for specific nucleic acid or protein sequences in seconds. Functional proteomics is the study of protein expression in living systems, considered in a functional context. This allows us to better understand how protein networks become dysfunctional, which in turn enables the manipulation of protein functions and cellular phenotypes through the use of drug treatment, or genetic or environmental intervention
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Bio economy, bio based economy refers to all economic activity derived from scientific and research activity focused on biotechnology. In other words, understanding mechanisms and processes at the genetic and molecular levels and applying this understanding to creating or improving industrial processes. The term is widely used by regional development agencies, international organizations, and biotechnology companies. It is closely linked to the evolution of the biotechnology industry. The ability to study, understand and manipulate genetic material has been possible due to scientific breakthroughs and technological progress.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
2nd International Conference on Bioscience and Biotechnology, March 9-10, 2017 at Colombo, Sri Lanka; BIO World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology, July 23-26, 2017 at Montreal, Canada; BioTech 2017, June 13-17 at Prague, Czech Republic; European Federation of Biotechnology; Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB); The Biotech Research Society; Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC); Australia’s Biotechnology Organization (AusBiotech); New Zealand Biotechnology (NZBIO); Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
Bioethics is the application of ethics to the field of medicine and healthcare. It is also moral discernment as it relates to medical policy, practice, and research. The Term “bioethics” was first coined in 1971 (some say by University of Wisconsin professor Van Rensselaer Potter; others, by fellows of the Kennedy Institute in Washington, D.C.), it may have signified merely the combination of biology and bioscience with humanistic knowledge. Bioethics is the study of the typically controversial ethical issues emerging from new situations and possibilities brought about by advances in biology and medicine. Bioethicists are concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, and philosophy. It also includes the study of the more commonplace questions of values ("the ethics of the ordinary") which arise in primary care and other branches of medicine. The scope of bioethics can expand with biotechnology, consisting of cloning, gene therapy, life extension, human genetic engineering, astroethics and life in area, and manipulation of fundamental biology thru altered XNA, RNA and proteins.
Related: Biotechnology Conferences | Biotechnology Meetings | Biotechnology Conventions | Biotech marketing meetings | Biotechnology Research Conferences | Current events in biotechnology |Biotechnology Career Meetings
15th World Congress on Biotechnology and Biotech Industries Meet, March 20-22, 2017 at Rome, Italy; Biotechnology 2017, August 21-23, 2017 at Chicago, USA; 17th Euro Biotechnology Congress, September 25-27, 2017 at Berlin, Germany; Global Biotechnology Congress, Oct 9-11, 2017 at Auckland, New Zealand; 15th International Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology Conference, June 21-23, 2017 at London, UK.
Scope and Importance of Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, medicine, technology and other fields requiring bio-products. Modern use similar term includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. It is the integrated use of molecular biology, biochemistry and microbiology to achieve technological application of the capabilities of biological agents. Biotechnology is emerged as a science with immense potential for human welfare ranging from food processing, human health to environment protection. The field of biotechnology is constantly advancing. From finding ways to slow down the process of food spoilage, advancements in genetic engineering, to adapting organisms to clean up contaminated environments, new applications and biotechnological inventions are continuously being developed to help improve our world.
Modern biotechnology applies not only modern genetics but also advances in other sciences. However, there is a third revolution that is just emerging, which is nanotechnology. The development of techniques to visualize and manipulate atoms individually or in small clusters is opening the way to an ever-finer analysis of living systems. Nano-scale techniques are now beginning to play substantial role in the application of biotechnology.
World renowned experts and intellectuals agree that biotechnological innovation is the foundation-stone of our future, and a ‘game changer’. It is anticipated that it will underpin our economy and provide solutions to intractable problems of human and animal diseases, climate change, fuel alternatives, food security as well as improving our quality of life.
Why Tokyo, Japan??
Annual Meeting on Biotechnology and Bioeconomy is going to be held in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo Metropolis is the capital of Japan and one of its 47 prefectures. The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world. It is the seat of the Emperor of Japan and the Japanese government. The population of the special wards is over 9 million people, with the total population of the prefecture exceeding 13 million. The prefecture is part of the world's most populous metropolitan area with upwards of 37.8 million people and the world's largest urban agglomeration economy.
Tokyo is in the Kanto region on the southeastern side of the main island Honshu and includes the Izu Islands and Ogasawara Islands. In 2015, Tokyo was named the Most Live able City in the world by the magazine Monocle and it ranked first in the world in the Safe Cities Index.
Biotechnology Societies and Associations in World
Biotechnology Society of Nepal
Society for Experimental Biology
Japan Bio industry Association
National Biotechnology Organizations
The Society for Biotechnology
Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agro chemistry (JSBBA)
Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB)
German Association of Biotechnology Industries
European and International Biotech Industry Associations
Texas Healthcare& Bioscience Institute
Biotechnology Industry Organization (BIO)
The BioIndustry Association (BIA)
The European Generic Medicines Association (EGA)
The Controlled Release Society (CRS)
The Institute of Clinical Research (ICR)
International Society for Biological and Environmental Repositories (ISBER)
The European Association for Bioindustries
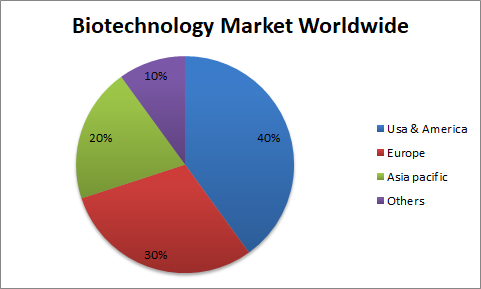
Biotech Market in World
Biotech Market in Asia Pacific
The biotechnology industry in the Asia-Pacific region is attracting more and more private investments in the wake of immense growth opportunities and vast untapped biotech markets, according to a new report from RNCOS titled Asia Pacific Biotechnology Market (2011-2016). Identifying the future growth potential of the industry, the governments of different countries in the Asia-Pacific region are taking up various initiatives to promote research in this region. Overall, the Asia-Pacific biotech market is expected to spur future growth in the global biotechnology market.
Biotech Market in Japan
The biotechnology industry occupies an important position in 21th century Japan. The industry was valued at 2.75 trillion yen (approx. $ 34.5 billion USD) in 2012.The current of open innovation promotes the growth and activities of Japanese biotechnology companies (currently over 500) and the growth of their licensing out of contracts. The competitiveness of the Japanese biotechnology industry is largely underpinned by the country’s high share of biotechnology patents filed under PCT and the high amount of biotechnology R&D expenditures in the business sector. The Japanese government recognizes biotechnology as a key driver of future economic growth and strongly supports both domestic biotech initiatives and its global development. The regenerative therapy especially the therapy using iPS cells is accentuated to support by them. Collaborative development of Japanese biotechnology business with foreign activities is greatly welcomed under the circumstances.
Japan Ranks 2nd in the world
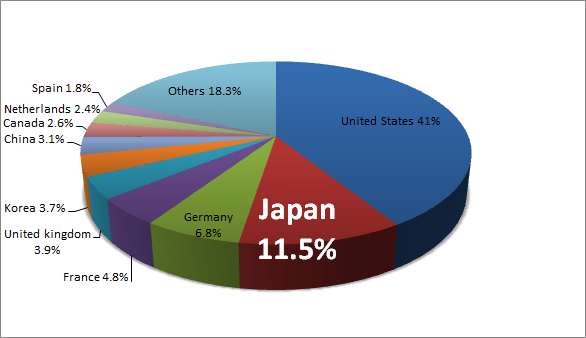
Biotech in Middle East
Biotechnology market is currently its trade deficit is nearly US$8 billion, its external debt market is expected to grow to nearly US$31.6 billion during the forecast period 2011-2020
Biotech Market in Europe
Biotechnology and life sciences contribute to the modernization of European industry. They are used in a variety of industrial sectors such as healthcare and pharmaceuticals, animal health, textiles, chemicals, plastic, paper, fuel, food, and feed processing. Taking advantage of biotechnology helps the EU economy grow and provides new jobs, while also supporting sustainable development, public health, and environmental protection. The biotech industry in Europe spends nearly $7.32 billion in R&D and $23.2 billion in revenue. Around 20% of the total marketed medicines, and as much as 50% of all drugs that are in the pipeline, are all healthcare biotech products. The European biotech industry provides employment to approximately 95,000 people.
Biotech Market in USA
The USA biotechnology market size was valued at USD 270.5 billion in 2013 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.3% growing to the increasing demand for diagnostics and therapeutics solutions such as recombinant technology, red biotechnology, and DNA sequencing. The increasing prevalence of diseases such as cancer, hepatitis B, and other orphan disorders is expected to serve as a high-impact rendering driver for this industry in recent period. Rising government initiatives owing to high significance towards growth of the economy are expected to boost the biotechnology market growth over the forecast period.
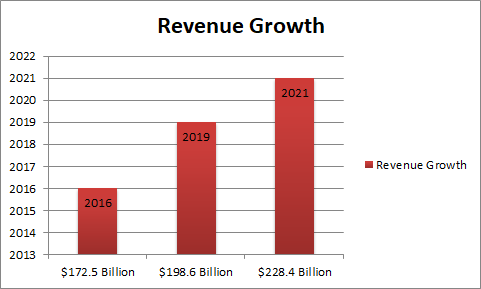
Biotech Market Revenue
The Global Biotech Flavors Market is poised to grow at a CAGR of around 10.7% over the next decade to reach approximately $228.4 billion by 2021. This industry report analyzes the market estimates and forecasts of all the given segments on global as well as regional levels presented in the research scope. The study provides historical market data for 2016, forecasts from 2016 till 2021
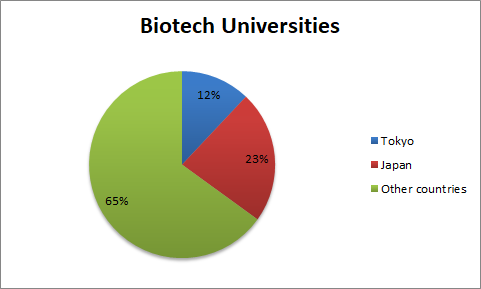
List of universities in Tokyo offer Biotechnology
University of Tokyo
Tokyo Institute of Technology
Sophia University
Ochanomizu University
Waseda University
Keio University
List of Universities in Japan offer Biotechnology
Osaka University
Kansai University
Kyoto Sangyo University
Mie University
Shinshu University
Yamaguchi University
Shizuoka University
University of Fukui
Chiba University
Doshisha University
Hokkaido University
University of Tsukuba
Iwate University
The University of Tokushima
Yokohama City University
Nagasaki University
Kanazawa University
Okayama University
Hiroshima University
Kobe University
Tohoku University
Top Universities in world offer Biotechnoogy
Harvard University
University of Oxford
Massachusetts Institute of technology (MIT)
University of Cambridge
Stanford University
University of California
Yale University
University of Toronto
Perking University
University of Melbourne
Dalian University of Technology
Liaoning Normal University
Washington University
University of British Columbia
McGill University
The University of Hong Kong
Cornell University
National University of Singapore
University of Pennsylvania
University of London (UCL)
University of Chicago
University of Michigan
Duke University
The University of Queensland
Aarhus University
University of Gottingen
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Lund University
York University
- Biotechnology
- Medical Biotechnology
- Agricultural Biotechnology
- Environmental biotechnology
- Industrial biotechnology
- Bio process engineering
- Plant Biotechnology
- Molecular engineering
- Enzyme engineering
- Food Biotechnology
- Marine Biotechnology
- Nano Biotechnology
- Stem cell biology
- Tissue engineering
- Animal biotechnology
- Algal biotechnology
- Fermentation technology
- Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
- Genomics & Proteomics
- Bio economy
- Bio ethics and Regulation
- Journal of Biotechnology & Biomaterials
- Journal of Bioprocessing & Biotechniques
- Journal of Bioengineering & Biomedical Science
























































































































