
Antibiotics 2018

Theme: Improving World Health with Antibiotics
Meetings international officially welcomes all the participants from all over the world to attend international conference on World congress on Antibiotics scheduled in Rome, Italy during August 13-14.The point of Antibiotics 2018 is to unite Scientists, Researchers, teachers, Business delegates, students and research associates to tell about their experience and knowledge and also about the research they are working on, The main theme of the conference is “Improving world health with antibiotics”.
Track 1: Antibiotic Therapy
Many antibiotics are also effective against protozoans and fungi; some are toxic to humans and animals also, even when given in therapeutic dosage. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as common cold or influenza, and may be harmful when taken inappropriately.
The issue of antibiotic misuse and resistance has become large one. Antibiotics are life-saving therapy. Many general principles can help you make decisions about initiating, selecting, and discontinuing antibiotic therapy.
Outpatient therapy: This treatment lasts for about 28 to 90 days, depending upon what you are expecting from the treatment. Hospital therapy: Hospital therapy includes rapid administration of “Broad” empiric therapy.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 2: Antibiotic Resistance & Prevention
Antibiotic resistance has been emerged as an important determinant of outcome for patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). This is mostly due to the administration of inadequate antimicrobial treatment, which is most repeatedly related to bacterial antibiotic resistance. World Health Organization (WHO) classified Antibiotic resistance as a serious hazard and no longer a signal for the future. Antibiotic resistance is now among each and every part of the world and its touching everyone regardless to the age. When infections become resistant to first-line drugs, more costly therapies must be suggested. Bacteria have become resistant to antimicrobial agents as a result of chromosomal changes or the exchange of genetic material via plasmid. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, and staphylococci, organisms are now resistant to all of the older antibiotics.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 3: Pharmacology of antibiotics
Knowledge of how the body handles a drug, in particular to find out absorption, distribution and excretion, aids to contribute analytical dose regimes which give therapeutic combinations but keep adverse reactions to a minimum. The two significant features of the structure of penicillin are the (3-lactam ring and the side-chain). If any changes in the side-chain give rise to variation in resistance to gastric acid and variation in antibacterial spectrum. In general, expanding the length of the side-chain increases resistance to gastric acid and increases the antibacterial spectrum. The pharmacological study of a new antibiotic is usually not a very simple one, mainly if it is adulterated. Penicillin & streptomycin when first used clinically were crude dugs and it has been more in case of penicillin than streptomycin.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 4: Applications of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are used to treat or avoid bacterial infections, and sometime protozoan infections. When an infection is suspicious of being responsible for an illness but the responsible pathogen has not been detected, an experimental therapy is adopted. This includes the administration of a broad spectrum antibiotics depending on the signs and symptoms detected. Antibiotics are used to treat or prevent some types of bacterial infections. They aren't effective against viral infections, such as the common cold or flu. Antibiotics should only be used to treat conditions that aren't serious but are unbelievable to clear up without the use of antibiotics such as moderately severe acne.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 5: Antibiotics for Emerging & Re-Emerging diseases
Antibiotic agents can in some cases connect with different drugs or substances. This implies it can have an impact that is diverse to what you anticipated. A few antibiotics should be brought with sustenance, while others should be gone up against a void stomach. You should dependably read the patient data handout that accompanies your prescription. Antibiotic drugs increase skin affectability to both normal and mimicked light. Manhandle of antibiotic agents can incite to bacterial protection.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 6: Antibiotics in Oncology
For patients getting chemotherapy, there is an expanded danger of disease because of a low WBC tally (neutropenia) caused by a dangerous impact of chemotherapy on the bone marrow. Anti-infection prophylaxis in afebrile neutropenic patients fundamentally decreased allâ€cause mortality. The most critical diminishment in mortality was seen in surveying prophylaxis with quinolones. For patients with hematologic tumor, anti-microbial prophylaxis is emphatically prescribed, ideally with a quinolone. Prophylaxis may likewise be considered for patients with strong tumors or lymphoma.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 7: Interaction & Side Effects of Antibiotics
For patients getting chemotherapy, there is an extended hazard of a low WBC count (neutropenia) caused by an unsafe effect of chemotherapy on the bone marrow. Against disease prophylaxis in afebrile neutropenia patients on a very basic level diminished allâ€cause mortality. The most basic diminishment in mortality was found in looking over prophylaxis with quinolones. For patients with hematologic cancer, against microbial prophylaxis is determinedly recommended, mainly with a quinolone. Prophylaxis may similarly be considered for patients with solid tumors or lymphoma.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 8: The Next Generation Approach of Antibiotics
Next generation sequencing is a powerful tool to compare the whole genomes and analyze the single base pair variations found within the antibiotic resistant genes. For patients getting chemotherapy, there is an extended hazard of a low WBC count (neutropenia) caused by an unsafe effect of chemotherapy on the bone marrow. The most basic diminishment in mortality was found in looking over prophylaxis with quinolones. Prophylaxis may similarly be considered for patients with solid tumors or lymphoma.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 9: Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance
Some bacterial species are by nature consistently safe, some consistently defenseless, and some incorporate both vulnerable and safe strains. Common Antibiotic safe strains of microscopic organisms are an expanding danger to creature and human wellbeing. Gained bacterial antibiotic protection can come about because of the change of ordinary cell qualities, the securing of protection qualities, or a blend of these two. The most well-known protection components utilized by microorganisms incorporate enzymatic corruption.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Track 10: Alternative to Antibiotics
Plants, food, and home grown tinctures have been utilized as characteristic antibiotic agents to treat illness for a considerable length of time. Antibiotics can give a transient answer for helping you recover. Oil of oregano as a herb that has antibiotic properties, also said to have mitigating properties, which can help lessen side effects of joint inflammation and hardened joints. Coconut oil contains a supplement called lauric corrosive, which has common antimicrobial, antiviral, and antifungal properties and lauric corrosive is viewed as a characteristic antibiotic for candida, yeast diseases, hacks, irritation, and warts. Garlic is said to be one of the world's most seasoned, best regular antibiotic. Grapefruit seed extricate is said to have common antibiotic properties; it contains a sort of cancer prevention agent called polyphenols.
Antibiotics conference | Antibiotic workshops | Antibiotic resistance conference | Multidrug resistance conference | Next generation Antibiotic conference | Antibiotic symposiums | Antibiotic world congress | Antibiotic therapy workshops | Antibiotic resistance symposiums
Why Rome, Italy?
Italy has been established in 1996, with support from a core group of 20 healthcare professionals from distinct hospitals in the region. The group has been seeking collaboration from township and local institutions, and got official recognition from the Ministry of Health. Rome has the grade of a global city. It has been ranked in 2016 as the 13th-most-visited city in the world, 3rd most visited in the European Union, and the most famous tourist highlight in Italy. Its historic centre is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. Monuments and museums located in rome such as the Vatican Museums and the Colosseum are among the world's most visited tourist places receiving millions of tourists a year.
Importance & scope of Antibiotics:
The first antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. He found that some bacteria which he had left in a petri dish had been killed by naturally occurring penicillium mould. Since the discovery of penicillin, many other antibiotics have been identified or developed. Antibiotics, also known as antibacterials, are drugs that wipe out or slow down the growth of bacteria. They include a range of powerful drugs used to treat diseases caused by bacteria. Infections caused by viruses, such as colds, flu, most coughs, and sore throats cannot be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics dosn’t treat viral infections because they can't destroy viruses.
Because of antibiotic overusage, certain bacteria have become resistant to the most powerful antibiotics available today, this is called Antibiotic resistance. Some of the strongest Antibiotics include cephalexin, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, azithromycin etc ; Natural antibiotics include honey, cabbage, grapefruit seed extract, extra virgin coconut oil etc. Antibiotics show effect after 24-48 hours. If not the bacteria could be resistant to that antibiotic, or it was not a bacteria. Side effects of antibiotics include allergy, type 1 hypersentivity reactions, toxic effects, disbacteriosis. Mechanism of action of antibiotics include inhibition of cell wall synthesis, disruption of cell membrane, inhibition of protein synthesis, inhibition of nucleic acid.
Global business & research value on Antibiotics:
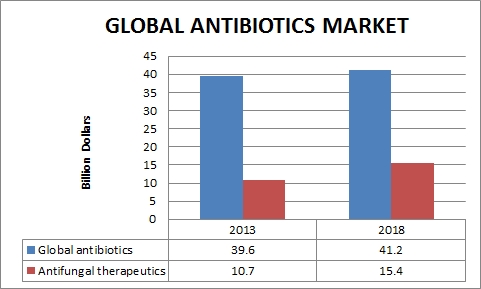
Recent years have seen a comeback of international involvement about the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance, and in particular Antibiotic resistance. A recent guess is that by 2050 Antibiotic resistance could cost 10 million premature deaths per year and $100 trillion in cumulative economic damage. It is scientifically challenging to discover new antibiotics that are active against the antibiotic-resistant bacterial species of current clinical concern. There are three main boundaries we need to overcome in order to achieve success, the complexity of the science and clinical trials process, the need for transformational diagnostics, the challenging commercial environment. Antibiotic-resistant infections are already being epidemic in the U.S. and all over the globe. There are many companies preparing antibiotics and there are many other antibiotics in the market such as aminoglycoside antibiotics and it covers about 79% of the global demand.
Global antibiotic societies/research centres:
Asia:
- Australian society of antimicrobials
- Australian society for infectious diseases
- Chinese society for Microbiology (CSM)
- The Philippine society for Microbilogy
- Israel society of Microbilogy
Europe:
- The world alliance against antibiotic resistance (WAAAR)
- Antibiotic research UK (ANTRUK)
- BEAM alliance (Biotech’s from Europe innovating in anti-microbial resistance)
- ReAct – Action on antibiotics
USA:
- Alliance for prudential use of antibiotics
- Centre’s for disease control and prevention
- U.S Food and drug administration
Global antibiotic universities:
Asia:
- University of Tokyo
- National University of Singapore (NUS)
- Kyoto University.
- University of Hong Kong (HKU)
- Peking University.
- Seoul National University (SNU)
- National Taiwan University (NTU)
- Osaka University.
Middle East:
- King Saud university
- Cairo University
- King Abdulaziz University
- Alfisal University
- Ain Shams University
Europe:
- University of Vienna
- Vienna University of technology
- Johannes Kepler University Linz
- Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz
- KU Leuven
- Ghent University
USA:
- University of California
- Duke University
- Stanford University
- Columbia University
- Washington University
Global funding bodies:
- Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
- The Royal Society
- The Gatsby Charitable Foundation
- European Molecular Biology Organisation
- European Research Council
- European Science Foundation
- Public health agency of Canada
- Stop TB Partnership
- World Health Organization
Future scope of antibiotics:
The efficacy of the world’s antibiotics is quickly decaying – the drugs we’re using to treat diseases are working less . If we proceed at this rate without interruption, we may find that there will not be a single antibiotic left to treat any type of bacterial infection. . But there’s good news, we are not likely to continue at this scale. The world is familiar of the problem and there are many organizations, governments, and concerned citizens working hard to avoid a worst-case scenario.
Conclusion:
Antibiotics are the medications which treat infections caused by bacteria. These doesn’t kill viruses hence viral infections are not treated by using antibiotics. The over usage of antibiotics may cause or promote antibiotic resistance. Bacteriostatic antibiotics inhibit or limit the growth of bacteria by interfering with bacterial protein production, DNA replication or by celluar metabolism. Over usage of antibiotics develops antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Each and every time a person takes antibiotics, sensitive bacteria (bacteria which are useful) are killed, but resistant bacteria are left to grow and multiply. This is how repeated use of antibiotics can increase the number of drug-resistant bacteria. So antibiotics are used within limits then there will be no bacterial resistance.
- Antibiotic Therapy
- Antibiotic Resistance & Prevention
- Pharmacology of Antibiotics
- Applications of Antibiotics
- Antibiotics for emerging & Re-Emerging Diseases
- Antibiotics in Oncology
- Interaction & Side Effects of Antibiotics
- The Next Generation Approach of Antibiotics
- Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance
- Alternative to Antibiotics
- Medical Microbiology Reports






















































































































